Master of Science in Speech-Language Pathology
book_2 Learning Mode: Residential
Program Overview
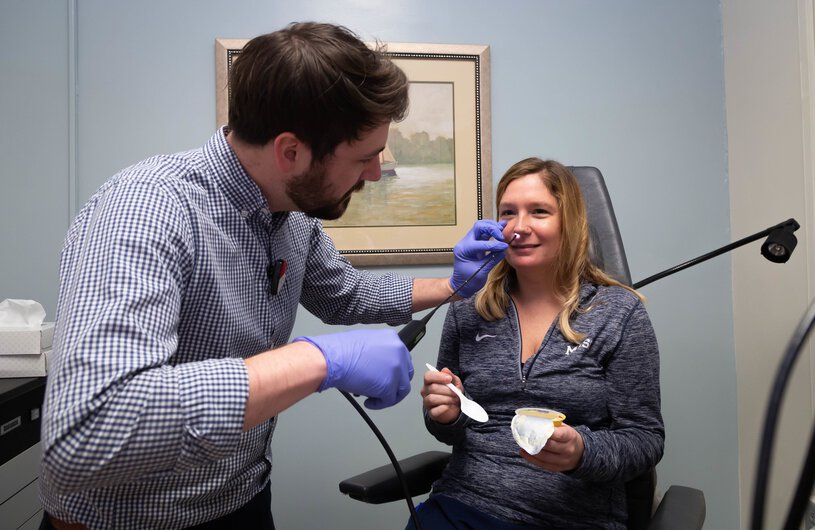
The Master of Science in Speech-Language Pathology (MS-SLP) program at MUSC provides students with a unique educational experience, rooted in clinical practice, and prepares them for a career across the scope of practice in speech-language pathology, with an emphasis on the knowledge and skills to treat complex medically based communication and swallowing disorders. Students build foundational knowledge early, then hone skills through interactive classrooms and progressive clinical rotations.
Application Timeline
Fall 2026
Jul 1, 2025 – Dec 15, 2025
For the 2024-2025 academic year.
Success you can measure
From national recognition to student satisfaction and real-world results, these numbers reflect the value and impact waiting for you in our program.
Learning Experience
Experience hands-on clinical practice under expert faculty, rooted in evidence-based methods and designed to foster confident, compassionate clinicians.
Inside the Program
The Master of Science in Speech-Language Pathology program prepares students to work as an entry-level clinical speech-language pathologist (SLP) upon graduation. While students will be prepared to work across the entire scope of practice, including schools, our program has an emphasis on medical speech-language pathology. The curriculum is designed to focus on clinical training. Students are taught foundational knowledge early on, and they hone their clinical skills via interactive classrooms and clinical rotations as they progress in the program.
As a comprehensive academic health sciences system, MUSC provides students with access to top-notch facilities and faculty. SLPs provide care in both hospital and outpatient clinic settings to a diverse patient population including pre-term babies in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), inpatients after stroke or traumatic brain injury, and patients with head and neck cancer. Students will have the opportunity to learn from and work alongside practicing clinicians in a variety of patient cases throughout the program, including during their didactic course work.
The curriculum is organized around specific competencies: diagnosis, management and treatment of communication, and swallowing disorders; anatomy and physiology; research methods (including quantitative, qualitative, and single-subject methodologies, as well as evidence-based practice); interdisciplinary practice; professional issues and ethics, the legal foundations of health care delivery and practice. The program is designed to ensure that graduates possess the knowledge, skills, and abilities to perform competently and proficiently.
The program curriculum adheres to Council on Academic Accreditation in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology (CAA) standards for program accreditation and is in accordance with Council for Clinical Certification in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology (CFCC) standards for professional certification. It is organized around specific competencies: diagnosis, management and treatment of communication, and swallowing disorders; anatomy and physiology; research methods (including quantitative, qualitative, and single-subject methodologies, as well as evidence-based practice); interdisciplinary practice; professional issues and ethics, the legal foundations of health care delivery and practice. The program is designed to ensure that graduates possess the knowledge and abilities to perform competently and proficiently.
Curriculum
The curriculum is designed to complement the natural progression of student learning throughout the program. Programming has been specified to focus on disorders most commonly seen in medical speech-language pathology (i.e., dysphagia and aphasia), while providing high-quality content and experiences across the scope of practice. By the end of the first year, students have completed coursework in all major disorders, with the remainder of the program focusing on specialized areas, research, and further development of clinical skills.
Our program incorporates best practices in clinician training common in other medical and allied health fields that are not commonly part of speech-language pathology training programs. In each course with clinical content, students are assessed on their knowledge, competencies, and clinical skills. To help students further develop their clinical skills, there are clinical rotations each semester. Each clinical rotation is paired with a didactic course to help students focus on specific skills and knowledge to ensure a thorough education and maximize their clinical experiences.
In addition to clinical rotations, one of the program’s core designs is to emphasize active learning in the classroom. Examples of active learning include case studies, role playing, small and large group discussion, practice of clinical skills, and debates. These activities ensure that students are engaged in practicing and refining their clinical skills throughout the entire curriculum, not just in a clinical setting. Active learning is commonly used in graduate education, which we incorporate into our curriculum.
| Year 1, Fall A (8/18/25-12/19/25) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SLP600 | Professional Issues: Ethical Considerations | 1 |
| SLP601 | Adult Swallowing | 5 |
| SLP602 | Neurogenic Language | 4 |
| SLP604 | Cog. Aspects of Communication | 2 |
| SLP605 | Clinical Rotation Didactic I | 1 |
| SLP606 | Clinical Rotation I | 1 |
| SLP623 | Tracheostomy & Ventilator | 1 |
| Semester Total | 15 | |
| Year 1, Spring (1/5/26-5/1/26) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SLP607 | Voice | 3 |
| SLP609 | Motor Speech | 3 |
| SLP614 | Patient Care & Counseling | 1 |
| SLP612 | Clinical Rotation Didactic II | 1 |
| SLP613 | Clinical Rotation II | 3 |
| SLP610 | Assessment | 3 |
| SLP621 | Multicultural Communication | 1 |
| IP711 | IP Foundations & TeamSTEPPS | 1 |
| IP### | IP Concentration of Choice | 1 |
| Semester Total | 17 | |
| Year 1, Summer A, Trailer (5/4/26-8/14/26) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SLP615 | Clinical Rotation Didactic III | 1 |
| SLP616 | Clinical Rotation III | 3 |
| SLP617 | Articulation & Phonology | 3 |
| SLP618 | Childhood Language: Birth to 5 | 3 |
| SLP620 | Pediatric Swallowing | 2 |
| SLP627 | Craniofacial Anomalies & Genetic Syndromes | 1 |
| SLP628 | Social Aspects of Communication | 3 |
| Semester Total | 16 | |
| Year 2, Fall A (8/18/25-12/19/25) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SLP631 | Communication Modalities | 1 |
| SLP625 | Clinical Rotation Didactic IV | 1 |
| SLP603 | Evidence Based Practice | 1 |
| SLP619 | Childhood Language: School Age | 3 |
| SLP622 | Clinical Rotation IV | 3 |
| SLP624 | Head & Neck Cancer | 2 |
| SLP632 | Hearing | 1 |
| Semester Total | 12 | |
| Year 2, Spring (1/5/26-5/1/26) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SLP636 | Professional Issues: Accreditation, Certification, Licensure, Specialty Recognition, & Advocacy |
1 |
| SLP637 | Clinical Rotation Didactic V | 1 |
| SLP611 | Practice Settings & Reimbursement | 1 |
| SLP629 | Intro to Research SLP | 3 |
| SLP626 | Clinical Rotation V | 3 |
| SLP630 | Comprehensive Exam | 1 |
| SLP633 | Fluency | 2 |
| Semester Total | 12 | |
| Year 2, Summer A, Trailer (5/4/26-8/14/26) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SLP634 | Clinical Externship | 9 |
| SLP635 | Clinical Externship Didactic | 1 |
| Semester Total | 10 | |
| Curriculum Total | 82 | |
Clinical Education
The program’s mission, vision, and guiding principles are rooted in the clinical preparation and training of SLPs. Our curriculum is uniquely designed to follow extant research and best practices. Each semester, beginning in the first semester, our students participate in a clinical experience spanning a broad spectrum of patients and settings. During students’ first semester, they are introduced to the adult acute care setting at the MUSC hospital. Every subsequent semester, students participate in a wide range of clinical experiences, which gives them many opportunities to be immersed in all aspects of patient care.
Each student’s participation in clinical activities is carefully coordinated by the program director, assistant director of Clinical Education and the supervising clinical educator.
Each clinical experience is paired with didactic/academic coursework that aligns with the clinical setting for the first four semesters. The intentional design of the academic coursework allows program faculty to define the optimal clinical learning experiences for each student depending on their interests and progression with both occupational and professional competencies. This integration between academic and clinical education allows students to make important connections between the classroom and the real-world clinical application.
Sample Clinical Rotations
The hours listed below are estimates of supervised clinical experiences in each semester. By the end of the program, all students must have earned a minimum of 400 total clinical hours.
- Semester 1: One day per week for five weeks; adult acute/inpatient with MUSC Health
- Semester 2: One day per week for seven weeks; adult inpatient or outpatient with MUSC Health or local facility (i.e., rehabilitation clinic, skilled nursing facility, home health, telehealth)
- Semester 3: One day per week for the entire semester; pediatric outpatient (i.e., early intervention/Babynet, home health, private practice, telehealth, outpatient clinic)
- Semester 4: Two days per week for the entire semester; school
- Semester 5: Two to four days per week; student interest anywhere in the country (adult/pediatric, inpatient/outpatient, school)
- Semester 6: Full-time between 30 and 40 hours per week, depending on the clinician’s schedule; full-time externship anywhere in the country
CARES Therapy Clinic
The Community Aid Relief, Education, and Support (CARES) Therapy Clinic is a student-run, pro-bono clinic offering physical, occupational, and speech and language therapy services to uninsured and underinsured individuals in the Charleston, South Carolina, community. Under the supervision of licensed speech-language pathologists, students work with clients on deficits in receptive and expressive language, motor speech, cognitive communication, and swallowing disorders. Clients visiting the clinic may have had a stroke, brain injury, hearing loss, developmental delays, a cleft palate, or cerebral palsy.
Become a Clinical Educator
Clinical educators serve an essential role in the education of our students. You can help prepare future speech-language pathologists and make a difference in our profession. The Division of Speech-Language Pathology is always looking for new opportunities to provide clinical education for our students. We are currently seeking clinical educators for all settings, including adult and pediatric medical placements in acute care, inpatient rehabilitation, hospital outpatient centers, skilled nursing facilities, home health, early intervention, as well as private practices and schools.
Serving as a clinical educator not only supports the next generation of health professionals but also comes with valuable personal and professional benefits, including:
- Free clinical supervision CEUs through Council of Academic Programs in Communication Science and Disorders (CAPCSD)
- Opportunity for adult medical CEUs through our biweekly rounds and other CEUs offered through the program
- Consultation with faculty on complex patient problems or involvement with research projects in the division
Clinical Educator Resources
- Calipso: Step-by-step instructions for educators
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA)
- Clinical Education and Supervision (ASHA)
- Required ASHA CEUs for Clinical Educators
Research Opportunities
Our program includes specifications grading (pass/no pass/high pass). The High-Pass option gives students the opportunity to go beyond the standard curriculum and immerse themselves in a topic or research area that sparks their passion. Through in-depth exploration and scholarship, students not only deepen their own expertise but also share their findings with peers and faculty—sparking conversation, collaboration, and fresh avenues for learning across the program.
Engage with our community
Connect through virtual information sessions, on-campus events, service outreach, and seminars that enrich both student learning and public health.
MUSC Doctor of Health Administration (DHA) Virtual Information Session
- calendar_today Wednesday, Feb. 4
Your path to admission
Discover key information about application steps and required documentation to help you move forward with confidence.
Eligibility Requirements
All applicants must:
- Possess a bachelor’s degree from a regionally accredited institution in the U.S. A specific major is not required. Applicants without a Communication Sciences and Disorders (CSD) undergraduate degree will need to complete additional prerequisite coursework.
- Complete a minimum of 12 hours of general education prerequisite coursework at a regionally accredited institution. In-person and online courses are accepted for all prerequisites. Courses do not need to be completed at the time of application but must be completed by matriculation. Applicants without a CSD undergraduate degree are required to take a minimum of 12 hours of CSD prerequisite coursework. Courses do not need to be completed at the time of the application but must be completed by matriculation. The program recommends applicants take as many CSD prerequisites as possible before applying.
- Complete 25 hours of observation in speech-language pathology by matriculation. Observation hours do not need to be complete at the time of application. We are unable to assist with finding observation opportunities. We accept in-person, telehealth, and Master Clinician Network opportunities for observation.
Minimum Abilities
At MUSC, we actively support all students to ensure their success in both academic and clinical settings. To support this goal, the university outlines the essential qualities and functional abilities required for participation in its educational programs. These include a range of observational, communication, motor, intellectual and behavioral skills necessary for safe and effective practice.
Prerequisites
| Prerequisite Coursework | Credit Hours |
|---|---|
| Anatomy & Physiology of Speech and Hearing† | 3 |
| Biology* | 3 |
| General Physics/Chemistry* | 3 |
| Normal Language Development† | 3 |
| Phonetics† | 3 |
| Social/Behavioral Science* | 3 |
| Speech and Hearing Science† | 3 |
| Statistics* | 3 |
* General Education coursework must be completed with a grade of 2.0 (C) or higher on a 4.0 scale. More specific information about courses that will satisfy these requirements may be found on ASHA’s website.
† CSD coursework must be completed with a grade of 3.0 (B) or higher on a 4.0 scale.
Additional Notes
- We do not accept credit for experiential learning for prerequisite credits.
- Dual enrollment courses and Advanced Placement (AP) courses are accepted for prerequisite credits so long as the course/credit appears on your college transcripts.
- Prerequisite courses must be fulfilled by separate individual courses.
Frequently Approved Prerequisites
Before applying, it's essential to ensure that any prior coursework meets the admissions requirements. MUSC provides a helpful reference list of frequently approved prerequisite courses to guide you in understanding which classes may satisfy your program's requirements. To explore the list, visit our Frequently Approved Prerequisites page.
Application Process
The following process outlines how and when your materials will be reviewed.
- Submit the CAPCSD Communication Sciences and Disorders Centralized Application Service (CSDCAS) application as early as possible. After fee payment and official transcripts are received, it usually takes four to six weeks to process and verify the application. Application, payments, and transcripts must be received by 11:59 PM ET on December 15, 2025. To ensure items arrive on time, it is essential that materials are sent several weeks before the deadline. All transcripts must be received by CSDCAS by December 15. Review by the MUSC SLP Admissions Committee will not begin until the application status has reached the Verified status.
- Complete the MUSC application.
- Once both applications are complete and the CSDCAS application has been verified, your application will be reviewed. Selected applicants will be contacted for an interview.
- Applicants who are invited to join the program will receive a letter of acceptance from the dean of the College of Health Professions by the end of March, with classes beginning in August.
Application Requirements
- CSDCAS Application: The following materials must be submitted through the CSDCAS application. You do not need to send any of the following information directly to MUSC.
- Completed application
- Letters of recommendation: All applicants must provide three references from professors or advisors who know you and your abilities. One professional reference from an employer is acceptable if you have been out of school for several years. References from family or friends are not accepted.
- Official transcripts from all institutions attended
- Responses to program-specific questions: All applicants must submit responses to the program-specific questions provided within the application.
- Prerequisite completion plan: Plans for completing prerequisite coursework and observation hours if not complete the time of application.
- Resume: Applicants must provide an updated resume detailing relevant academic and professional experience.
- SLP observation hours documentation: Applicants who have not completed 25 observation hours are welcome to download and use the MUSC Guided Observation Log.
- MUSC Application: All applicants must submit an MUSC application. Only the application is needed. You are not required to resubmit any supporting materials to MUSC, such as transcripts, references, or essays.
All information above must be received by the deadline to be considered for admission to the program. Without all materials, applications will be incomplete. It is the applicant's responsibility to review the progress of their application to ensure that all application materials have been submitted. Applicants are responsible for reviewing the progress of their CSDCAS application on the CSDCAS website.
International Applicants
Currently, MUSC’s MS-SLP program only accepts applications from U.S. citizens, permanent residents, or those holding other valid nonimmigrant visa classifications that allow participation in lawful study while in the United States. We are unable to accept international students that require I-20 issuance.
Why MUSC was the right choice
Hear why current students value MUSC’s supportive environment, interprofessional collaboration, and focus on personalized professional growth.



Funding your path forward
Tuition
| Fee Type | Fee |
|---|---|
| Application Fee (per application) | - |
| Matriculation Fee (upon applicant acceptance) | $500 |
Tuition and fees listed below are per semester unless otherwise noted.
| Tuition/Fee Type | Fall | Spring | Summer | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-state Tuition | $8,349 | $8,349 | $8,349 | - |
| Out-of-state Tuition | $12,465 | $12,465 | $12,465 | - |
| Program Fee | $500 | $500 | $500 | - |
Cost of Attendance
| Item | Year 1 | Year 2 | Est. Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Costs | |||
| Tuition - In-state/Out-of-state | $25,047/$37,395 | $25,047/$37,395 | $50,094/$74,790 |
| Fees | $1,800 | $1,800 | $3,600 |
| Health Insurance | $3,780 | $3,780 | $7,560 |
| Direct Costs Subtotal | $30,627/$42,975 | $30,627/$42,975 | $61,254/$85,950 |
| Indirect Costs | |||
| Housing/Food | $27,144 | $27,144 | $54,288 |
| Personal | $2,880 | $2,880 | $5,760 |
| Transportation | $3,240 | $3,240 | $6,480 |
| Books/Required Expenses | $7,490 | $6,906 | $14,396 |
| Indirect Costs Subtotal | $40,754/$40,754 | $40,170/$40,170 | $80,924/$80,924 |
| Total - In-state/Out-of-state | $71,381/$83,729 | $70,797/$83,145 | $142,178/$166,874 |
Disclaimer: The Estimated Total listed above reflects an approximation of educational costs for planning purposes only. Actual expenses may vary based on individual circumstances, program requirements and annual changes in tuition, fees and other costs. The Medical University of South Carolina reserves the right to adjust tuition, fees and other charges at any time without prior notice.
Scholarships
MUSC offers scholarships for which you may be eligible. Some are awarded based on academic achievement; others are awarded based on community service, for example. However, the majority of scholarships awarded at MUSC are based on financial need. This means that these scholarships are only awarded to students who need some financial assistance to cover the cost of tuition and fees. If you would like to be considered for a financial need-based scholarship, you must have an up-to-date Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) on file. Make sure you list the Medical University of South Carolina on your FAFSA form, along with MUSC's code: 003438. We encourage you to submit your FAFSA as early as possible. It is recommended to submit your FAFSA in January if you plan to enroll in the fall.
Click here to visit our scholarship application system to view a complete listing of MUSC scholarships.
Career Outlook
Student Outcome Data
Discover how our graduates excel with strong certification outcomes, effective employment pathways, and a meaningful impact in clinics and schools.
Completion Rates
The table below provides program completion data within the expected period.
| Reporting Period | # Completed | % Completed |
|---|---|---|
| Recent Year (2024-2025) | 40 | 100% |
| 1 Year Prior (2023-2024) | 41 | 98.78% |
| 2 Years Prior (2022-2023) | 41 | 100% |
Praxis Pass Rates
The table below provides the associated number of students that took the Praxis examination and pass rate for each year within the expected period.
| Reporting Period | # Taking the Exam | # Completed | % Completed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recent Year (2024-2025) | 38 | 38 | 100% |
| 1 Year Prior (2023-2024) | 41 | 39 | 95.12% |
| 2 Years Prior (2022-2023) | 33 | 32 | 96.97% |
Note: The Praxis examination reporting period is the testing year or examination cycle, not the year of graduation for test-takers. The data for each reporting period may include test-takers who graduated from the program within the prior three years.
Program Faculty

Christina Pelatti, Ph.D., CCC-SLP
Associate Professor
Dr. Christina Pelatti’s research expertise is in the areas of oral and written language in children, and she is particularly interested in examining factors that impact children with developmental (e.g., Down syndrome, DLD) and acquired (e.g., traumatic brain injury) disorders. Her work is interprofessional in nature, and her goal is to answer questions that are clinically applicable to professionals, children, and their families.

Lori-Ann Ferraro, Ph.D., MA, CCC-SLP
Associate Professor

Terry Hopkins-Rossabi, Ph.D., MS, CCC-SLP
Dr. Theresa Hopkins-Rossabi’s research focuses on swallowing function and outcomes in several patient populations. In addition, Dr. Rossabi’s research interests include competency-based education at the graduate level in the integration of knowledge and skills required for excellence in clinical practice.
Admissions Frequently Asked Questions
The GRE is not required.
The Admissions Committee examines each qualified applicant's portfolio, including the letters of reference, resume, responses to program-specific questions, and other admissions materials, and scores them. Experience related to speech-language pathology, strong letters of reference, volunteer/service activities, and leadership experience assist applicants in improving their profile scores. Applicants who score highly will be invited to interview with the program faculty.
MUSC does not offer leveling courses at this time. Applicants without a CSD degree must take a minimum of 12 hours of CSD prerequisite coursework. View the program admissions requirements.
Yes. You are not required to complete a minimum number of coursework hours to apply, but all courses must be completed by matriculation. We recommend that individuals complete as many Communication Sciences and Disorders prerequisites as possible before applying. If you have not completed all prerequisite coursework, you can provide your plans for completing the courses in your CSDCAS application.
No. Concurrent enrollment in prerequisite coursework is not possible. Prerequisite courses must be completed before beginning the program.
No. They do not need to be completed to apply, but they need to be completed by matriculation. You can provide your plans for completing the courses in your CSDCAS application.
The program will accept in-person, Telehealth, and the Master Clinician Network for observation hours. We cannot help with facilitating observation opportunities. We recommend contacting local private practices or clinics for observation opportunities.
Learning Experience Frequently Asked Questions
We accept 40-45 students each year.
New students begin coursework each fall semester. The start date is mid-August; students will participate in orientation, followed by the start of classes the following week and first-semester clinical rotation in the inpatient adult setting shortly after.
MUSC does not require the vaccine for enrollment into classes. However, due to clinical rotations at MUSC Health beginning in the fall semester, our students will be required to submit proof of COVID vaccination (among others) or documentation of declination for clinical access compliance.
Yes, we have a local NSSLHA chapter. You can follow them on Instagram to see what they have been up to. Each SLP cohort will also have representation in the College of Health Professions SGA & MUSC SGA Boards. In addition, there are a wide variety of special interest groups and other organizations for students to get involved.
We do not accept transfer credit for courses within the MUSC SLP curriculum. This includes advanced placement, transfer of credit, credit for experiential learning, and/or previous coursework or experience. page.
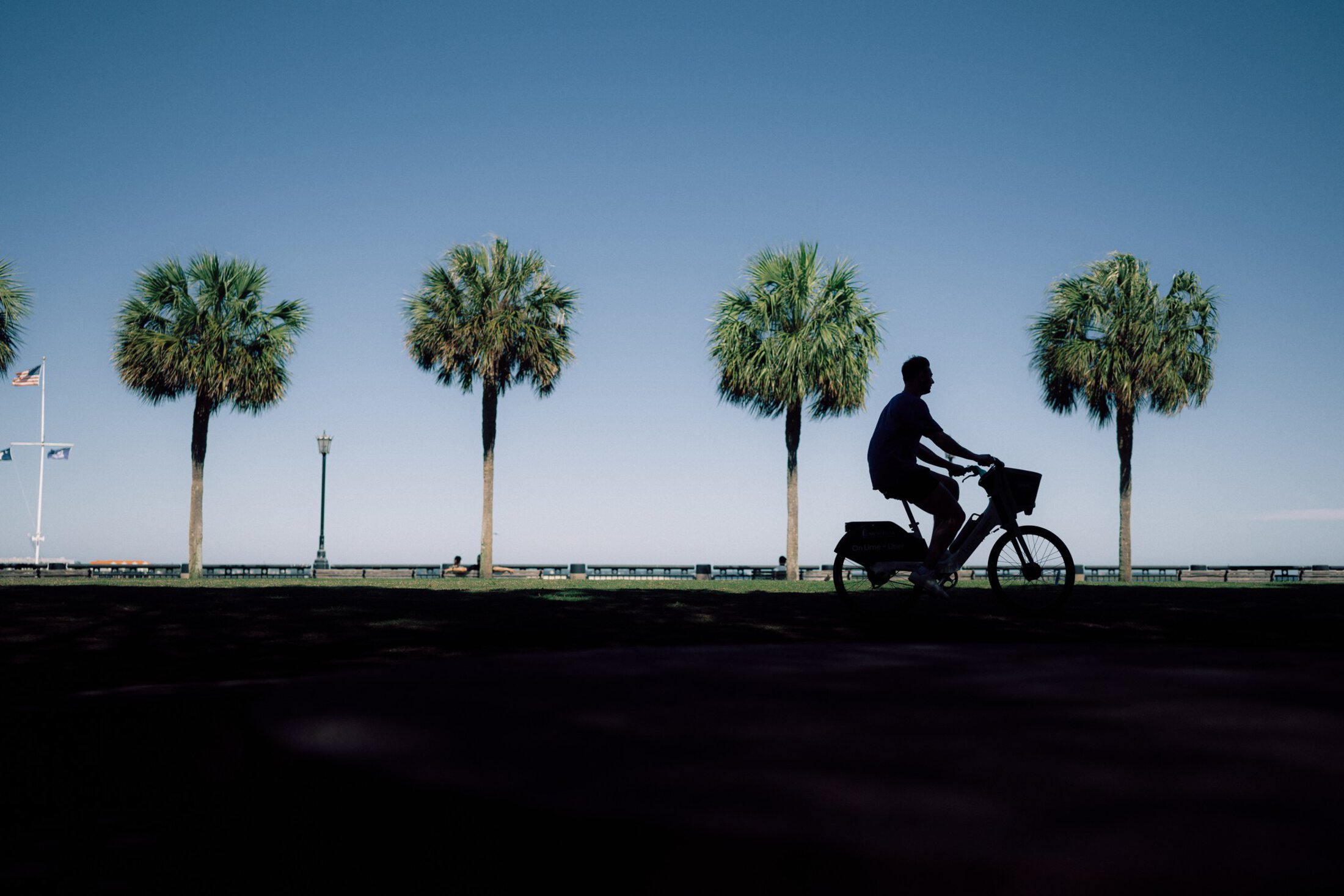

Living in Charleston
Charleston offers a unique blend of coastal beauty and modern convenience. With top-rated dining, scenic waterfronts and endless outdoor activities, the city offers an unmatched quality of life for residents, striking a balance between work and leisure.
Guided by Purpose and Principles
Experience a program built on excellence, innovation, inclusivity, and integrity, guiding your development as a reflective and ethical clinician.
Objectives
The MS-SLP program aims to prepare graduates to:
- Provide students with a high-quality education emphasizing clinical preparedness and excellence through its innovative educational design.
- Prepare students to enter the speech-language pathology (SLP) profession with a commitment to lifelong learning, leadership, unwavering professionalism, and advocacy.
- Integrate evidence-based practice and research knowledge across the curriculum and professional experiences to equip students to be critical thinkers.
Competencies
Upon completion of the MS-SLP program, graduates will be able to:
- Provide high-quality services within the scope of practice of speech-language pathology.
- Embed culturally responsive practices to individuals from all backgrounds, family members, caregivers, and members involved in care.
- Foster the well-being of those we serve with humility and dignity.
- Apply sound problem-solving, critical thinking, and clinical reasoning skills to patient/client diagnosis, treatment, and management.
- Work in a collegial and collaborative manner with professionals when supporting clinical practice, research, and learning opportunities in speech, language, swallowing, and cognitive-communication disorders across the lifespan.
- Develop and implement quality control measures and individualized data-based methods to ensure that SLP services are evidence-based.
- Adhere to the Code of Ethics of the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA).
- Adhere to legal principles and institutional practices applicable to clinical and research practice.
Vision
To be the preeminent leaders of the field of speech-language pathology.
Mission
The program will engage in curious and innovative discovery that advances clinical care, provides students with a research-based education that fosters clinical excellence, lifelong learning, and unwavering professionalism, and advocates for person and family-centered care to empower individuals and their communities.
Values
At the core of our program, we are guided by a commitment to the following principles and include them in all aspects of decision-making and implementation.
- Humanism (community, collegiality, collaboration, and dignity)
- Commitment to learning (critical inquiry and personal responsibility)
- Social responsibility
- Leadership
- Excellence in clinical practice
- Innovation and creativity
Stories worth sharing
Stay informed about inspiring student achievements, faculty innovations, and community partnerships that make a real difference.



Accreditation & Recognition
The Master of Science in Speech-Language Pathology program at the Medical University of South Carolina is accredited by the Council on Academic Accreditation in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology of the American Speech-Language Hearing Association (ASHA); 2200 Research Boulevard, Suite 310, Rockville, Maryland, 20850; telephone: 800-498-2071 or 301-296-5700; website: https://caa.asha.org.